Graph Representation: Adjacency Matrix
When it comes to implementing the Graph interface, there are several ways to represent graphs, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
The choice of representation will have implication on the efficiency of various operations of the Graph ADT. Depending on the problem at hand, you go for one representation or another.
Here, we'll see two ways to represent graphs: the adjacency list vs the adjacency matrix.
An adjacency matrix is a $N \times N$ matrix (array), where element $(i,j)$ is 1 if and only if the edge $(v_i, v_j)$ is in $E$.
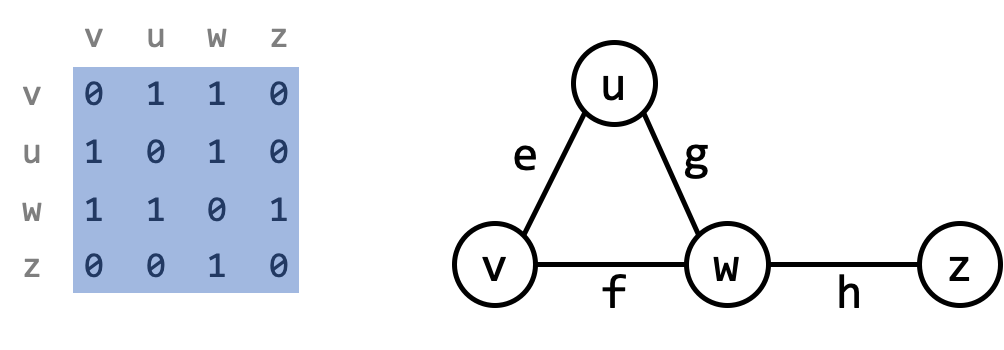
Thus an adjacency matrix takes up $O(N^2)$ storage.
Resources
- Representing Graphs by Khan Academy.