Task 2
Notice the CumulativeMaxList interface in the task-2 package.
For element $k$ of a given list, the cumulative maximum is the maximum of elements at positions $1$ through $k$.
In this context, the first element in the list is at index $1$; i.e. it is a $1$-based indexed list. (As opposed to $0$-based indexed lists where the first element is stored at position with index $0$.)
For example, consider the sequence below:
$$ 5, \; 2, \; 4, \; 3, \; 7, \; 1 $$
Here is the cumulative maximum sequence for it:
$$ 5, \; 5, \; 5, \; 5, \; 7, \; 7 $$
Suppose a CumulativeMaxList stores the sequence in the given example and a client invokes the operation insertAt(4, 8). Here is the state of the data structure after the operation is performed:
index | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
get(index) | $5$ | $2$ | $4$ | $8$ | $3$ | $7$ | $1$ |
getMaxAt(index) | $5$ | $5$ | $5$ | $8$ | $8$ | $8$ | $8$ |
The LinkedCumulativeMaxList is a linked-list implementation of the CumulativeMaxList. Notice its static nested Node class. It has two reference variables: next pointing to the next node and maxPrev pointing to the node among the preceding nodes that contains the cumulative maximum value. For example, here is a schematic representation of values $5, 2, 4, 3, 7, 1$ stored in a LinkedCumulativeMaxList:
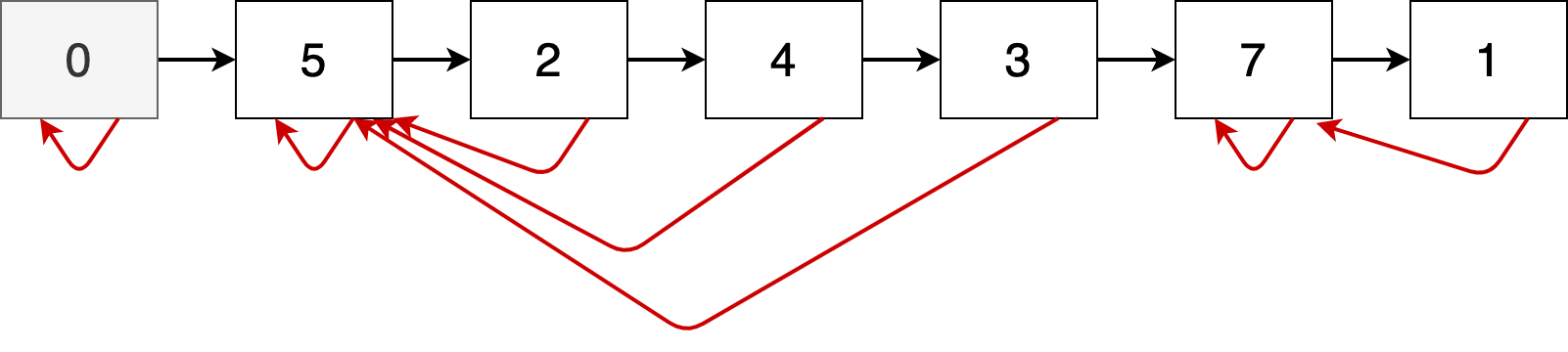
In the figure above, the red arrows show maxPrev reference variables. Notice the first node with value $0$. An assumption is made to simplify the solution here: the data structure only stores positive integers. The node with value of $0$ is inserted to the list in the constructor and does not count towards the elements of the LinkedCumulativeMaxList. This node is always there! You don't remove it, nor overwrite it; its existence makes it easier to treat index parameter as a $1$-based position index. It also makes for fewer edge cases; e.g. an empty LinkedCumulativeMaxList is not "really" empty, it contains the sentinel node with value $0$:

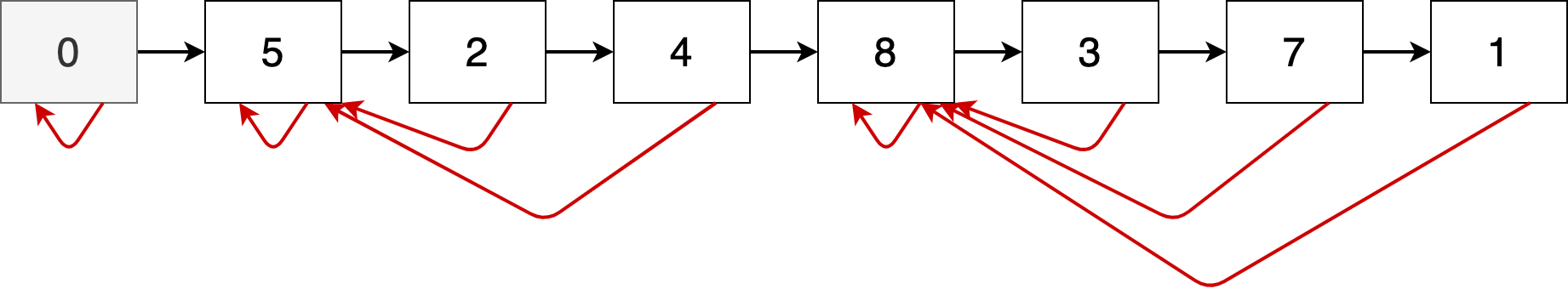
To make sure that you understand how LinkedCumulativeMaxList works, draw a schematic representation of its internal state similar to those above for the values $5, 2, 4, 8, 3, 7, 1$ stored in that order.
Solution
Your task is to complete the implementation of insertAt inside the LinkedCumulativeMaxList class. Make sure to test your implementation against tests in CumulativeMaxListTest. Those tests well also help you to better understand how this data structure works.