Merge Sort: Analysis
The merge sort runs in $O(n \lg n)$ time.
Justification:
- The number of times the merge sort divides a sequence is the number of times $n$ can be halved: $O(\lg n)$.
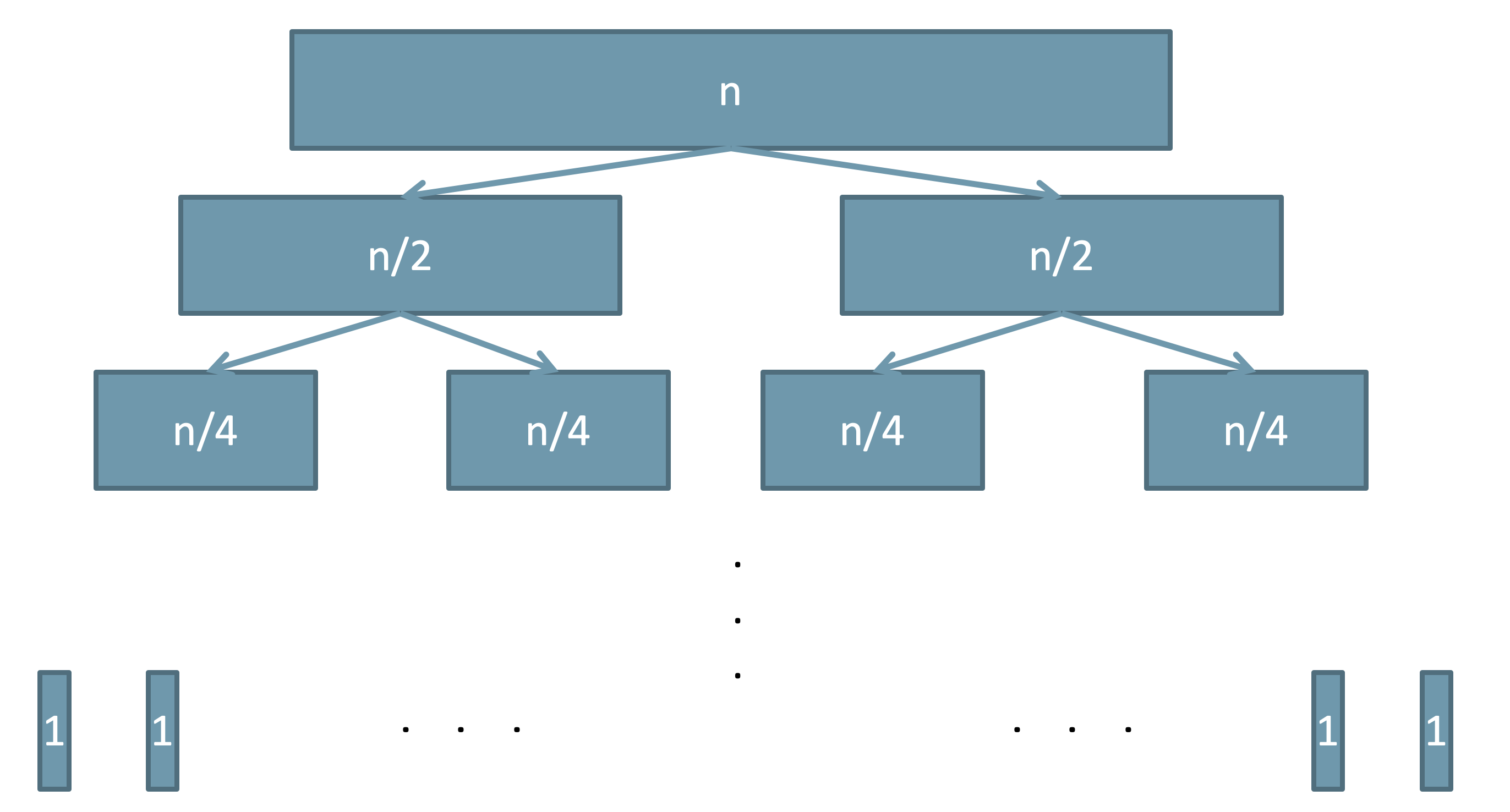
- The number of times merge sort merges the subsequences is equal to the number of sub-sequences. Therefore, the merging part also has $O(\lg n)$ steps.
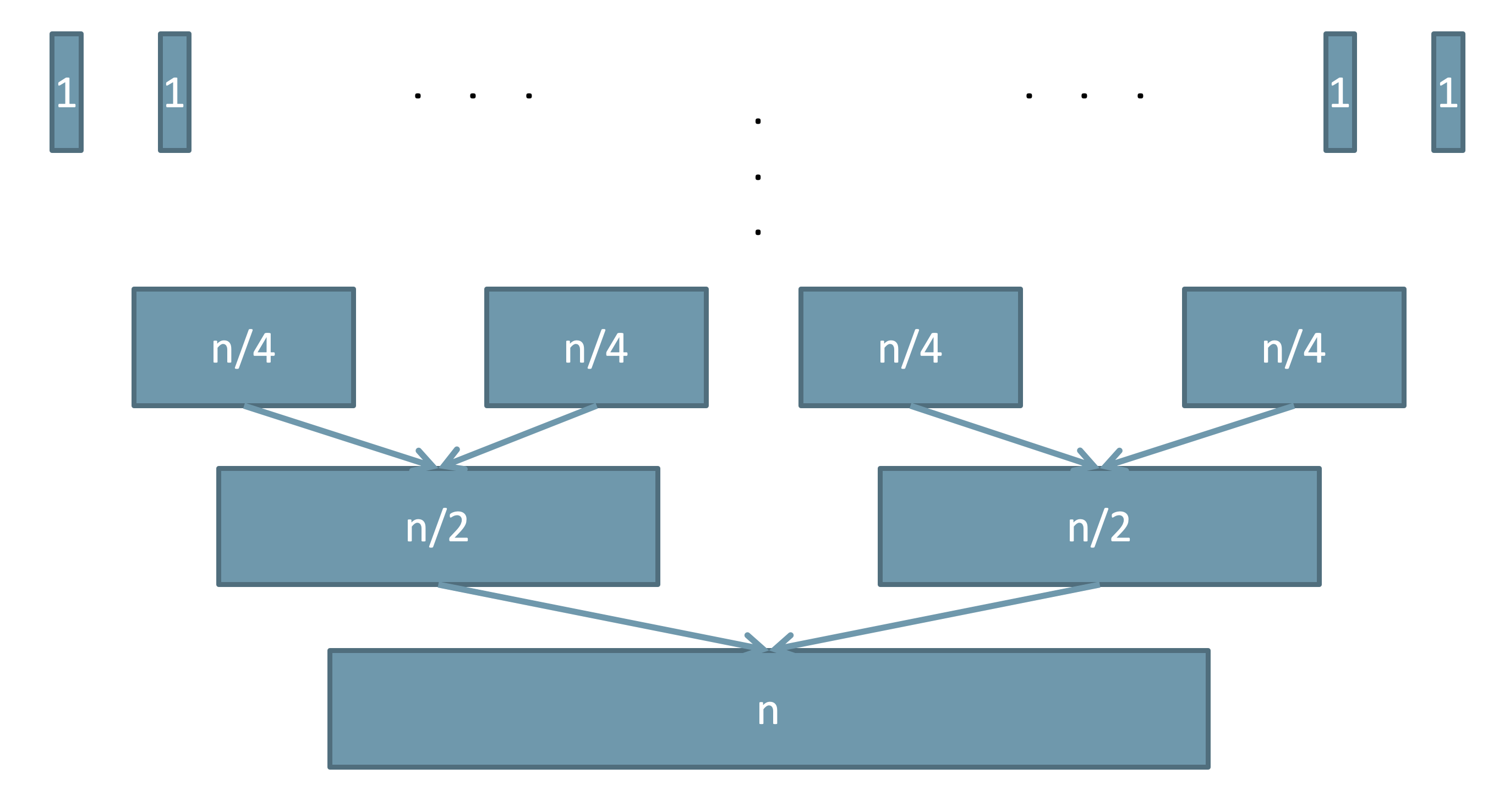
-
Since the merge process is linear, each merge steps goes over all $n$ elements.
-
So the total running time for the merge sort algorithm is $O(n \lg n)$,
Formal Proof
A more formal proof can be constructed by writing the runtime of merge sort as a recurrence relation $T(n) = 2T(n/2) + \theta(n)$ and showing $T(n) \in \theta(n \lg n)$.
If you want to look this up, search for "the master theorem for divide-and-conquer recurrences" and look up "case 2". This is, however, beyond the scope of this course.
Resources
- Wikipedia's entry on Merge sort: Analysis.
- Wikipedia's entry on Master Theorem.